Computer Support FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why can’t I log in?
- How can I type umlauts with a US keyboard?
- How do I find additional programs under Ubuntu?
- Which email programs can I use and how do I configure them?
- How can I set up email forwarding?
- Why does Acrobat Reader report that I have too little space on my hard disk?
- How can I start Mathematica without owning a license?
- What do I do if Firefox does not start or displays an error message on startup?
- Is Latex free of charge and is Latex also available for other operating systems?
- Can I change the color palette of the terminal?
- Where can I find or create (new) announcements?
- How can I restore old data from my home directory?
- Are there projectors and what do I need to consider?
- What should I do?
- FAUbox and Gigamove
Login
1. Why can’t I log in?
If you are unable to log in, please check the following:
- When entering the password, you can change the layout of your keyboard at the bottom center (default is US).
- After entering the account name, check whether accessibility features (bottom right: blue circle with white figure) are deactivated.
- Quota may have been exceeded: see here.
- If you still have problems with logging in, please contact room 01.330 or call 67335
Ubuntu
1. How can I type umlauts with a US keyboard?
This works best with the Compose button: usage of the compose-key.
As there is normally no such key on keyboards, you can instruct Ubuntu to make another key (which you do not otherwise need) the Compose key. To do this, open the Dash (Windows key) and look for the Keyboard setting. There you can click on Typing under the Shortcuts tab. Here you can set the Compose Key.
2. How do I find additional programs under Ubuntu?
The default user interface is now Unity. The Dash helps to find programs:
- The Dash is called up with the Windows key. Alternatively, you can also click on the Ubuntu logo in the top left-hand corner of the screen.
- Standard programs (e.g. Firefox, Thunderbird) are already offered for launch in the Dash.
- In the Dash search bar, however, you can also simply search for applications etc. (e.g. “mail”, “web”, “terminal”, “document”).
- It is also possible to click through anywhere using the “More Apps” button.
- The “taskbar” is located on the left edge of the screen. If it is hidden, move the mouse pointer to the left edge to show it again.
- If you use a program frequently, it is worth anchoring the program in the taskbar: right-click on the icon in the bar and select “Keep in Launcher”.
- If you are using the terminal, you can open a Gnome terminal directly with Ctrl+Alt+t.
1. Which email programs can I use and how do I configure them?
- Thunderbird settings:
| Outgoing Server | mail.math.fau.de |
| Port | 587 |
| Connection Security | STARTTLS |
| Authentication Method | Normal Password |
| Server Settings | imap.math.fau.de |
| Port | 143 |
| Connection Security | STARTTLS |
| Beim ersten Starten stets Confirm Security Exception wählen | |
- mutt : muttrc, msmtprc muttrc and .msmtprc now still be customized with personal data.
- Webmail: math.fau.de/webmail, mail.math.fau.de/webmail
Setting an incorrect ‘reply to’ email address may result in your emails no longer being delivered.
The webmailer is recommended because it can be used with any browser and from anywhere, and does not require any setup.
2. How can I set up email forwarding?
If the following information is not sufficient for setting the forwarding/absence message, or if further problems occur, please contact us: problems@math.fau.de
Roundcube Webmail – Forward messages
If you would like to automatically forward messages from your e-mail account to a specific e-mail address, proceed as follows:
- At the top right you will find an icon for settings. Click on this
- A menu with various areas will then be displayed on the left-hand side. Click on “Server settings”
- You will then see your various filters under the Filter tab
- Here: Click on the plus “Add filter” at the bottom left.
- Enter a unique filter name.
- Under “For incoming messages”, click on “All messages”.
- Under “…perform the following actions”, select “Redirect message to” in the left option button. In the text field, enter the email address to which the messages should be redirected.
- Make sure that the “Filter enabled” tick is set and your filter is therefore applied. Click on “Save” to create your new filter.
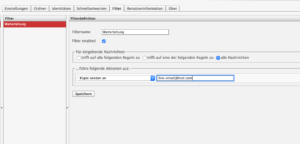
The new filter appears at the end of the filter list. Select it (marked in red) and move it (“Move up” symbol above the filter list) to the appropriate position in the order of the filter list. To deactivate the filter again, uncheck “Activate filter” and click on “Save”.
Important note: To avoid complications when using the webmailer filters, please deactivate or delete the outdated filter rule. After the forwarding filter, all subsequent rules in your filter settings are deactivated! If these are to be applied, they must be moved further up.
Quelle: www.rz.uni-greifswald.de
Roundcube Webmail – Set up Vacation Mail
To set up a Vacationmail, proceed as follows:
- At the top right you will find an icon for settings. Click on this.

- A menu with various areas will then be displayed on the left-hand side. Click on “Server settings”
- You will then see your various filters under the Filter tab
- Under “…perform the following actions”, select “Reply with message” in the left option button.
- Write a message content and possibly a message subject.
- (optional) Under “How often should messages be sent (in days):” you can set the number of days after which the sender receives the Vacation Mail from you, regardless of how many emails they send you during this period.
- Make sure that the “Filter deactivated” checkbox is not ticked.
- Click on Save. The filter applies from this point on.
Note: Do not delete this autoresponder after your absence, but simply switch it off by ticking the “Filter disabled” box. You can then simply switch it back on again for later use.
Printer
1. Is it possible to print double-sided?
Each printer can also print double-sided (printer-nn-ds).
2. Can you print in color?
The printers printer-68, printer-81 and printer-82 can also print in color (printer-nn-color or printer-nn-color-ds).
3. Can films be printed?
Yes, this is possible, initially only on a Lexmark printer. Proceed as follows:
- First open the manual tray at the front of the printer, pull it out and flip it open.
- Then insert the film with the edge to the right up to the marking.
- Im Dokumentenbetrachter wählt man dann unter “paper source” das manuelle Fach und unter “paper type” transparencies aus.
- Then send the print job.
- : Do not prompt, paper loaded.
4. How to print .docx files?
- Click on “Export as PDF…” under File,
- Then click on “Export”.
- Then open the .pdf file with evince or okular and print the file as usual.
5. How do I cancel my own print jobs?
If you want to delete a print job that has already been sent to the printer, proceed as follows:
- Click on the Ubuntu icon at the top left of the launcher and then enter printing.
- Click on it – a window opens with the available printers.
- Select the “Printer” tab in the program bar and then click on “View Print Queue”
- All print jobs that are being printed or are in the queue are now displayed in the window that opens.
- Here you can now select your job and delete it.
Programs
1. Why does Acrobat Reader report that I have too little space on my hard disk?
This is an error in Acrobat Reader. The home directories are located on a file system that is currently 30 terabytes in size. When trying to determine the free space there, a 32-bit counter overflows. The operating system warns of this, but Adobe interprets the warning incorrectly.
Solution: Save the file on the local hard disk (e.g. in “/tmp”) and then move it to the home directory. Or use another PDF viewer instead of Acroread, e.g. evince or okular.
2. How can I start Mathematica without owning a license?
You only have to tell Mathematica the license server of the RRZE. To do this, click on “Other ways to activate”, then “Connect to a network license server” and enter
license2.rrze.uni-erlangen.de
in the text field. Confirm with “Activate” and accept the license conditions.
3. What do I do if Firefox does not start or displays an error message on startup?
This can have various causes:
- For students: You use more than 3 GB in your home!
Solution: Use Ctrl-Alt-F1 to switch to a virtual console. Log in there and delete unnecessary files. The 3.0Gb can be queried with the command “du -sh .”. Genaue Anleitung - A session was not closed in accordance with the rules.
Solution: Change to “cd .cache/mozilla/firefox-esr/xxx.default/” (xxx=name of your profile) and remove with “rm -r .parentlock” the .parentlock file. - The profile has been damaged by a crash, for example.
Solution: Firefox has to be closed. Open inside your shell the profilemanager with “firefox -ProfileManager” and add a new profile. Saved Bookmarks can be restored via “Bookmarks/Show All Bookmarks/Import and Backup/Restore/Choose File…” editing or importing: go to “.cache/mozilla/firefox-esr/xxx.default/bookmarkbackups/” and select your file.
4. Is Latex free of charge and is Latex also available for other operating systems?
Yes just google “latex OPERATINGSYSTEM”.
More informations about Latex: www.ctan.org.
A quick Introduction is here.
Webseite
1. Where can I find or create (new) announcements?
No further announcements can be made using the old announcement script.
To do this please use this: Kalender des Departments.
The Frontend-Account for this you get by neuss@math.fau.de.
A Caldav server has been set up in the Department of Mathematics. This is a network application that communicates with various types of calendar programs (Thunderbird/Lightning, Evolution, AppleCalendar, Microsoft Outlook, etc.) and provides calendars that users can integrate into their personal calendars.
Sicherungskopien
Das zfs
In addition to various data backups, we have been using zfs for some time now. This means that every user has access to an image of their HOME directory at any time. To access the old files, proceed as follows:
- There is a folder called .zfs/snapshot in the directory of employees and students. This folder is not visible, which means that it can only be accessed from the terminal and not using the file browser. For employees:
cd /home/np1/staff/.snapshot/zfs
For students:
cd /home/np1/stud/.snapshot/zfs
- Here you will find images of the HOME directory at various points in time. Backups are performed once per hour, per day, and per week. The length of time for which they are stored depends on the type of backup. For example, hourly backups are kept for one week, while weekly backups are kept for six months. The state of the HOME directory at the time of the backup is always saved. This means that if changes are made within an hour, they cannot be retrieved. The format of the snapshots is: year-month-day-hourminutesecond. For example, if an employee wants to access data in the HOME directory from the weekly backup of August 10, 2013, the entry is:
cd snap-weekly-1-2013-08-10-030146
Then navigate to your HOME directory:
cd /home/np1/staff/.snapshot/zfs/snap-weekly-1-2013-08-10-030146/username
All files are now stored there in their state of the date.
- Caution! There is a new system on the CIP computers and some of the employees’ computers. Snapshots are taken every six hours. The procedure for data recovery is the same, but the snapshots are no longer called snap-weekly-1-2013-08-10-030146, but auto-20190820-060000. The new format is therefore auto-DATE-TIME.
File recovery
These are only images. This means that no files in the .snapshot/zfs/snap-weekly-1-2013-08-10-030146 folder can be changed, only read. However, it is possible to copy files from the snapshot to another directory and then use them there as normal.
cp /home/np1/staff/.snapshot/zfs/snap-weekly-1-2013-08-10-030146/username/testdatei /home/np1/staff/username/testdatei_2013-08-10
alternativ
cp /home/np1/staff/.snapshot/zfs/snap-weekly-1-2013-08-10-030146/username/testdatei ~/testdatei_2013-08-10
Useful information
- If you want to see how different versions of a file differ at different points in time, you can do so with the command diff:
diff testdatei1 testdatei2 | less
However, if you want to redirect the result to a file:
diff testdatei1 testdatei2 > differenzen
In the following example, testfile1 from the backup is compared with testfile2 located in the HOME directory. Using the diff command, the files are compared line by line; the differences are then specified.
diff /home/np1/staff/.snapshot/zfs/snap-weekly-1-2013-08-10-030146/username/testdatei1 ~/testdatei2 |less
Legen Sie sich einen Symlink in Ihrem HOME-Verzeichnis an:
ln -s /home/np1/staff/.snapshot/zfs/snap-weekly-latest/username backup-snap-daily
Other
1. Are projectors available and what do I need to bear in mind?
The building services department (Tel.: 27777) administers the projectors in the practice rooms and lecture halls.
Apparently, the order (starting up the projector, connecting, etc.) plays a role. Therefore, follow this order:
- Beamer and Laptop turn on;
- if both of them are set up you can link them;
2.My problem is not listed. What should I do?
Please send an email to: problems@math.fau.de.
3. Passwortgenerator (Seite reload für neues Passwort):
F4s:UbA+jJ8eJkQcgBrsYVqy
padhbxsrzugt
4. FAUbox and Gigamove
Computer Support FAQ
System Administration Glossar
account
An account on a “UNIX”-System. It consists of the pair of username and user ID, also called login and UID.
BSD
Berkeley Software Distribution
Family of mostly free unix derivates like FreeBSD, OpenBSD and NetBSD.
Bash
(Bourne-again shell) is the standard shell in many unix and linux systems. Contrasting to the PowerShell/PowerShell Core is the bash not object-oriented, but purely text-based.
C
is the programming language in which the platform independent part of the Linux kernel and most of the applications has been developed.
CLI
(Command Line Interface). A programme that enables the user to issue commands to the operating system. Under Linux the CLI is realized in the form of the different shell-implementations.
Compiler
A compiler serves as a tool for the creation of programmes. More precisely, it translates source code into object files.
Copy-On-Write
Describes a feature of file systems where blocks are not over-written directly, but instead a copy of the new data is stored in a different block. After finishing a new block, the corresponding pointer is adjusted. Hence, in the case of a system crash during the write-operation no inconsistent file system state is created. Only the data that was written in that moment would be lost, but the previous version of the block is still intact. Apart from that, this concept makes the easy and fast creation of snapshots possible.
CPU
(Central Processing Unit). The primary micro-processor. A processor is an (albeit very small and freely) programmable arithmetic unit, i. e. a machine or electrical circuit that controls other machines or electrical circuits according to the instructions it is being passed.
Dataset
(in the context of ZFS) is a term for ZFS-file systems, volumes and snapshots. Datasets are organised in a hereditary hierarchy and always assigned to a zpool. They serve as structuring unit of the pool and can be tailored to many different applications. The compression, check sum algorithm, logical block size and many more features and properties of any dataset can be changed individually by setting corresponding parameters. All datasets share the storage space of the whole pool, hence they should not be considered as a partition with its own storage space.
Daemon processes
processes running in the background and mostly performing special tasks.
Device (file)
A device interface that is mapped to a device file in the virtual file system. These files usually reside under the directory /dev.
Debian
Debian Linux is also a collaboratively developed free operating system. Debian GNU/Linux is based on the basic system tools of the GNU project and the Linux kernel.
ext2/ext3/ext4
The file systems primarily used under linux. The newer ext3 featuires journaling, in contrast to ext2, however it is backwards-compatible. Using an ext2-driver one can still access an ext3 partition. ext4 is has been developed as successor to ext3.
FIFO
(First-In-First-Out). A FIFO is a queue. Data that has been written into it has to be retrieved in the same order.
Firewall
A computer or application that protectes the local network from attacks from the internet.
FQDN
(Fully Qualified Domain Name). The full domain name of a system, consisting of hostname and domain. The full name of a (web) domain is called the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). In that case, it is an absolute address.
The FQDN www.example.com. consists of: 3rd-level-label. 2nd-level-label.
Top-Level-Domain(com). and hence is: www.example.com
FTP
(File Transfer Protocol). A protocol for the communication with file servers.
GPL
(GNU General Public License). Licence under which linux and a lot of other free software is distributed.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol).
A protocol describing the interaction with web-servers.
HTTPS
HTTPS (HTTP Secure) is an encrypted version of HTTP. Most of the times it uses SSL (en-US) or TLS in order to encrypt the whole communication between a client and a server. This safe connection enables clients to safely exchange sensitive information with the server, like e. g. in online banking or online shopping.
Interpreter
An interpreter executes a script written in a programming language without having to compile it beforehand.
ISO 9660
This standard describes a file system for CD-ROMs and DVDs. Typical characteristics are the limits on the length of filenames. Also there is no information about the file owners and permissions.
Journaling
In journaling file systems, every transaction is logged, so that after a crash the often-times cumbersome repair of the file system can be omitted.
Kernel
The kernel is the core component of the operating system and responsible for important tasks like process and memory management or supporting the hardware.
Kernel-Module
Loadable kernel modules (LKM) are components that can be dynamically integrated into the kernel and often provide driver code. Thanks to such LKMs a re-compilation of the kernel is often not necessary.
Kernelspace
Memory region in the RAM for the kernel and all kernel modules, like hardware drivers.
LKM
(Loadable Kernel Module). See Kernel-Module.
Linux
is an operating system based on the linux (operating system) kernel an free GNU software. Linus was developed in 1991 by the Finn Linus Torvalds on the basis of the operating system UNIX.
Multitasking
Ability to execute multiple processes simultaneously.
Multiuser
A multiuser systems is an operating system that is capable of providing and keeping seperated working environments for multiple users.
NFS
The Network File System (NFS) is a protocol developed by Sun Microsystems which allows accessing files over a network connection.
NNTP
NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is a transfer protocol for new in newsgroups. It is used e. g. in Usenet.
NTP
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a standard for the synchronization of clocks in computer systems over packet-based communication networks. NTP uses the connection-less transfer protocol UDP or the connection-oriented TCP. Is was developed specifically to make the transmission of reliable time stamps possible over networks with variable packet runtime.
Open Source
Movement for the promotion of free software. Free software is defined by its free use and the availability of the source code.
Proxyserver
A proxy server is a server between many clients and one server. In general its task is to buffer requests so that the server is not being overloaded.
Process
A process in Linux is ideally representing a running programme. Apart from the executable programme code also the environment, consisting but not restricted to shell variables, is included in this concept.
Pseudo File System
A file system that typically resides in memory and has to be access via a pseudo interface. Examples are procfs and swapfs.
Quota
Disk Quota (quite literally) is a limit for the storage on storage devices like hard drives, that a single user or group of users can use. It limits the storage use of a user.
RAM
(Random Access Memory). The main memory.
ROM
(Read Only Memory). A memory that can only be written once. It is e. g. installed on the mainboard for storing the BIOS.
SMB
A protocol for file shares in a network. Primarily used in the Windows ecosystem.
SMTP
(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). The standard protocol for sending E-mail.
Snapshot
freezes the state of a filesystem at a certain point in time. If data in the file system is changed, both the current version and the version of the snapshot are stored. At a later time either the state of the snapshot can be restored ore single files of the snapshot can be accessed for recovery purposes.
Secure Shell (SSH)
is a protocol and the corresponding client and server programmes for establishing an encrypted network connection. SHH features mutual authentication and an encrypted file transfer. Initially only for UNIX-based systems, there are nowadays also implementations for Windows and others.
Swap
Parts of the main memory relocated onto the hard drive.
Syscall
A system-call, i. e. a call of a particular kernel function by a programme running in user space.
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
The TCP/IP-protocol family consists of many important protocols for network
communication.
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a network protocol which defines
how data should be exchanged between network components.
Unlike the connection-less UDP (User Datagram Protocol) in TCP a connection
is established between the end-points of a network connection (sockets). Using that connection data can be transmitted in both directions. Most of the times TCP is stacked onto the IP (Internet Protocol). That is why sometimes people (mostly imprecisely) talk about a “TCP/IP”-protocol.
Ubuntu
also Ubuntu Linux, is a Linux distribution derived from Debian. The name comes from the Nguni philosophy of ubuntu, which means something in the direction of “humanity to others.”
Userspace
Part of the RAM which is used for all programmes and data that are not directly associated to the kernel. Hence, these programmes have no access to the memory region of the kernel.
VFS
(Virtual File System). The virtual file system forms the basis of file system management. All other file systems are integrated by so-called mount points and are hence transparent to the user.
WLAN
(Wireless LAN). Connect to the network over radio connections.
X11
The X window system 11 release 7 (X11R7) provides a graphical user interface for Unix systems.
Zombie-Process
A process which has already terminated but still resides in memory. That way, the parent process can still evaluate the return status of the process later even though it has been neglected at the time.
ZFS
ZFS is a transactional file system developed by Sun Microsystems.
zpool
Concept of ZFS. In practical applications several physical storage devices are pooled into logical units, the zpools, which can optionally be configured more fail-safe. In order to generate a pool stretching over multple hard drives and then create partitions on it, only two relatively simple instructions are needed. Partitioning, creating the logical volume and subsequent mounting in an existing file systems is done automatically.

